Vaadin 14 - Troubleshooting
Sometimes Vaadin 14 fails mysteriously, which is very unfortunate: it now uses LOTS of JavaScript code, frameworks and tools. Those things are unfamiliar to server-side guys, and it’s really hard to tell what to do, should one of JavaScript toolchain fail.
This article remedies that, by listing a bunch of troubleshooting ideas and FAQs to follow and check out. We expect a basic knowledge of Vaadin toolchain here, please read the Vaadin: the missing guide article and the Vaadin Plugin under the hood article first.
What to verify server-side
To remove the possibility of random issues caused by corrupted node_modules
or inproper javascript package versions in package.json and package-lock.json/pnpm-lock.yaml,
it’s always good to start the bug hunting with the Vaadin Dance.
The Vaadin Dance
Sometimes Vaadin will fail to update package.yaml and package-lock.yaml with
new versions of npm modules (especially after a Vaadin version update),
or sometimes the node_modules becomes corrupted, or package.yaml will list
multiple versions of the same thing.
The best thing to do first is to perform the “Vaadin Dance” (akin to Eclipse Dance): delete all npm-related packages, npm config files and webpack config files and force Vaadin to start from the clean state. You can achieve this by deleting the following files:
node_modulespackage-lock.json(if using npm)webpack.generated.jspnpm-lock.yaml(if using pnpm)pnpmfile.js(if using pnpm)
Note: You can try to remove the
package.jsonas well, however for Vaadin 14.6 and newer it is not recommended to remove thepackage.jsonfile completely, as this can break your project if you have any frontend dependencies that have been added directly to it, like is the case with Fusion based views or theming related dependencies.
Note: With Vaadin Gradle plugin you can simply run the
vaadinCleantask to do this; there’s a feature request for Vaadin Maven Plugin for the same functionality.
Then run the prepare-frontend task, to re-create those files. Note that the node_modules
is populated later: either by Vaadin Servlet when running in development mode, or
by build-frontend when building for production.
Webpack build fails
If the failure is as follows:
ERROR [dev-webpack] (webpack) Module build failed: Error: ENOENT: no such file or directory, open '......\target\frontend\generated-flow-imports.js'
You must run the prepare-frontend goal/task before the build-frontend goal/task. Please review the
Maven/Gradle stdout log and check that the prepare-frontend goal/task has been run.
Clean pnpm-cache
When using pnpm, performing the Vaadin Dance may not be enough. The thing with pnpm
is that it manages a cache of downloaded javascript libraries (which is good and speeds
up the builds tremendously). However, node_modules is then populated not with actual files and folders,
but with symlinks to the pnpm cache instead. If by accident something has been
deleted from node_modules in an incorrect manner, it could be that the file got deleted
from the actual cache and the cache got corrupted.
In order to clear the cache and force pnpm to redownload everything, simply delete the
cache folder. The pnpm cache is located at $HOME/.pnpm-store on Linux/Mac.
Windows needs per-drive separated caches, since symlinks works only on the same drive.
Therefore, if your project is located on D:\ , the cache is located at D:\.pnpm-store.
After the .pnpm-store cache folder has been deleted, perform the Vaadin Dance
and rebuild the app.
Use npm instead of pnpm
pnpm is supposed to be a faster npm. However, the dependency resolution mechanism works a bit differently and it may cause issues with Vaadin 14. There are a couple of related bugs for Vaadin 14.5.x and lower: #10571, #10572, #11162.
For Vaadin 14, it’s recommended to use npm.
Gradle: use matching version of Vaadin and the Plugin
Please see the Compatibility Chart at Vaadin Gradle Plugin home page, to see which plugin version to use with which Vaadin version.
Gradle Plugin 0.7.0 may not work correctly with Vaadin 14.1.x; Gradle Plugin 0.6.0 may not work correctly with Vaadin 14.2+ (even though there are reports from users that it works just fine :-)
Use newest Vaadin
Use the newest Vaadin 14.x - there are also fixes with respect to the JavaScript toolchain; for example it could be that at some point Vaadin will be able to detect all breaks and issues and the Vaadin Dance will be unnecessary.
Development mode issues
If your webpack or npm is failing with a cryptic error messages, please make sure that
you have the flow-build-info.json on your classpath, and the npmFolder path
correctly points to your project location, and the frontendFolder correctly
points to the frontend/ folder in your project.
Production mode issues: make sure the necessary files are present
Make sure that all of the Vaadin files are present in the WAR/EAR/JAR archive, when
built for production mode via the build-frontend Plugin task:
- Most importantly, the
flow-build-info.jsonfile, located on classpath in theMETA-INF/VAADIN/config/package.- In a WAR archive it’s located in the
WEB-INF/classes/META-INF/VAADIN/config/folder; in a SpringBoot JAR it’s located inBOOT-INF/classes/META-INF/VAADIN/config/folder. - Make sure that it sets the following properties as follows:
"compatibilityMode": false, "productionMode": true, "enableDevServer": false - See Vaadin: the missing guide for an example of how the file should look like.
- In a WAR archive it’s located in the
- The
stats.jsonfile, located on classpath right next to theflow-build-info.json, in the same package. - The
META-INF/VAADIN/build/folder is populated as follows:
├── vaadin-2-18d67c4ccff7e93b081a.cache.js
├── vaadin-2-18d67c4ccff7e93b081a.cache.js.gz
├── vaadin-3-b0147df339bf18eb7618.cache.js
├── vaadin-3-b0147df339bf18eb7618.cache.js.gz
├── vaadin-4-ee1d2e45569f7eca4292.cache.js
├── vaadin-4-ee1d2e45569f7eca4292.cache.js.gz
├── vaadin-5-5e9292474e82143d0a27.cache.js
├── vaadin-5-5e9292474e82143d0a27.cache.js.gz
├── vaadin-bundle-19a00eae62ad7cddd291.cache.js
├── vaadin-bundle-19a00eae62ad7cddd291.cache.js.gz
├── vaadin-bundle.es5-b1c1a3cc054c62ad7949.cache.js
├── vaadin-bundle.es5-b1c1a3cc054c62ad7949.cache.js.gz
└── webcomponentsjs
├── bundles
│ ├── webcomponents-ce.js
│ ├── webcomponents-ce.js.map
│ ├── webcomponents-sd-ce.js
│ ├── webcomponents-sd-ce.js.map
│ ├── webcomponents-sd-ce-pf.js
│ ├── webcomponents-sd-ce-pf.js.map
│ ├── webcomponents-sd.js
│ └── webcomponents-sd.js.map
├── custom-elements-es5-adapter.js
├── LICENSE.md
├── package.json
├── README.md
├── src
│ └── entrypoints
│ ├── custom-elements-es5-adapter-index.js
│ ├── webcomponents-bundle-index.js
│ ├── webcomponents-ce-index.js
│ ├── webcomponents-sd-ce-index.js
│ ├── webcomponents-sd-ce-pf-index.js
│ └── webcomponents-sd-index.js
├── webcomponents-bundle.js
├── webcomponents-bundle.js.map
└── webcomponents-loader.js
Important: in the development mode, only the flow-build-info.json needs to
be present on the classpath. Vaadin Servlet will internally start a child webpack
process and will transfer all other files internally from webpack.
What to verify in your browser
You should at some point learn how to use your browser’s dev tools:
The Dev Tools is an IDE integrated into your browser which you use to:
- Debug javascript if something goes wrong
- Debug CSS layouts if something is positioned in an odd way
- Profile javascript when something is slow (e.g. when making a bug report to Vaadin Grid)
If you do not understand something in the text below, please refer to the Dev Tools guides above.
Quick tips
Press F12 in your browser to fire up dev tools, then head to the Network tab and reload
the page. It should download a bunch of files with the HTTP 200 OK result code, most importantly
the webcomponents-loader.js, vaadin-bundle-*.js and client-*.cache.js:
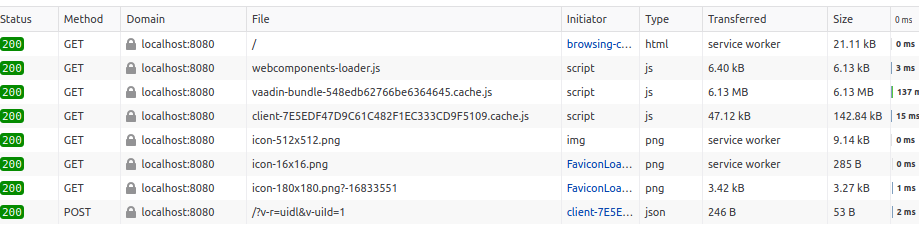
If those files fail to download then Vaadin Client side will not initialize at all. Most common incorrect HTTP codes are:
- 404 NOT FOUND: VaadinServlet is mapped to a different context root, or not mapped at all, or not activated by the servlet container at all.
- 403 FORBIDDEN: Make sure your Spring Security allows those files to pass through.
- Even on 200 OK, the web server may be lying to you.
Make sure that the content downloaded is valid; for example a request to
vaadin-bundle.jsactually downloads a JavaScript file and not for example a HTML login form. This happened to me on WebSphere; the request even succeeded with 200 OK!
If everything looks okay in the “Network” tab, go into the “Console” tab and make sure there are no “red” errors logged in the console, preventing Vaadin from initializing. Please see the Vaadin Troubleshooting - Browser article for more details on this.
Then, type this into the “Console” command prompt:
customElements.get("vaadin-button")
It should print something like class xyz { constructor }: that means that the
vaadin-button web component is registered properly. However, if it prints
undefined then there’s something very wrong going on and Vaadin hasn’t been initialized
on the client-side properly.
My component doesn’t work
It’s a good idea to confirm that your web component was loaded properly, via the JavaScript Console:
customElements.get("my-component")
If this prints undefined then:
- Verify that at least Vaadin has loaded properly, by trying
customElements.get("vaadin-button")as described above. If Vaadin is not loaded, see above for steps to take. - Please note that the
@HtmlImportannotation is completely ignored when Vaadin is running in npm mode - you need to use@NpmPackage()and@JsModule()instead. Also see below for tips. - (Development mode only): It could be that the webpack bundle was not rebuilt
properly. Try restarting the server - it could cause Vaadin Servlet
to notice changes, run
npm installand update thepackage.jsonandpackage-lock.jsonfiles. Also try to run theprepare-frontendtask/goal, to updatepackage.jsonandpackage-lock.jsonfiles. - Try to verify whether the npm module is present in both
package.jsonandpackage-lock.jsonfiles. If it’s not, maybe Vaadin classpath scanning doesn’t discover your@NpmPackage()-annotated class for some reason - make sure it’s on classpath. Alternatively, the values of the@NpmPackage()annotations are wrong - please double-check the values. - Try also performing the Vaadin Dance - it will force to re-generate
package.jsonandpackage-lock.jsonand the dependency may now appear. - TODO what else to check in this case?
If the customElements.get("my-component") command prints something like
class a { constructor(args) } then the web component is registered properly.
You can print the version of the web component, by typing
customElements.get("my-component").version
To call methods on the web component, simply select the DOM element in the
“Inspector” tab, and you can then reference the selected node via the $0 expression:
$0.click()
@HtmlImport doesn’t work
Yes, the @HtmlImport annotation is completely ignored when Vaadin runs in npm mode.
You either need to run Vaadin in compatibility mode, or simply replace the annotation
with @NpmPackage. For example, for <iron-form>, the following declaration
is not enough:
@Tag("iron-form")
@HtmlImport("frontend://bower_components/iron-form/iron-form.html")
public class IronForm extends HtmlContainer {}
The correct declaration which works both in compatibility mode and in the npm mode:
@Tag("iron-form")
@HtmlImport("frontend://bower_components/iron-form/iron-form.html")
@NpmPackage(value = "@polymer/iron-form", version = "3.0.1")
@JsModule("@polymer/iron-form/iron-form.js")
public class IronForm extends HtmlContainer {}
@HtmlImport/@JsModule/@JavaScript don’t work as expected
Please see the Vaadin 14 - difference between @JsModule and @JavaScript in npm mode article.
JavaScript compilation or Webpack fails
Please perform the “Vaadin Dance” as mentioned above - it could be that the package-lock
references an incompatible combination of package versions, or obsolete versions of
tools such as Babel.
In addition, try to delete the following folders (if they exist):
$HOME/.vaadin: contains a node.js distro downloaded by Vaadin; maybe it became corrupted?)$HOME/.pnpm-store(if you’re using pnpm): contains pnpm’s cache of JavaScript packages, maybe they somehow became corrupted)
Others
Search the Vaadin Flow Bug tracker for any issue you will find in the JavaScript console. If the issue is not yet reported, please report it so that it can be investigated (or Vaadin’s error messages can be improved).
Please let me know at mavi@vaadin.com and I’ll add more tips.